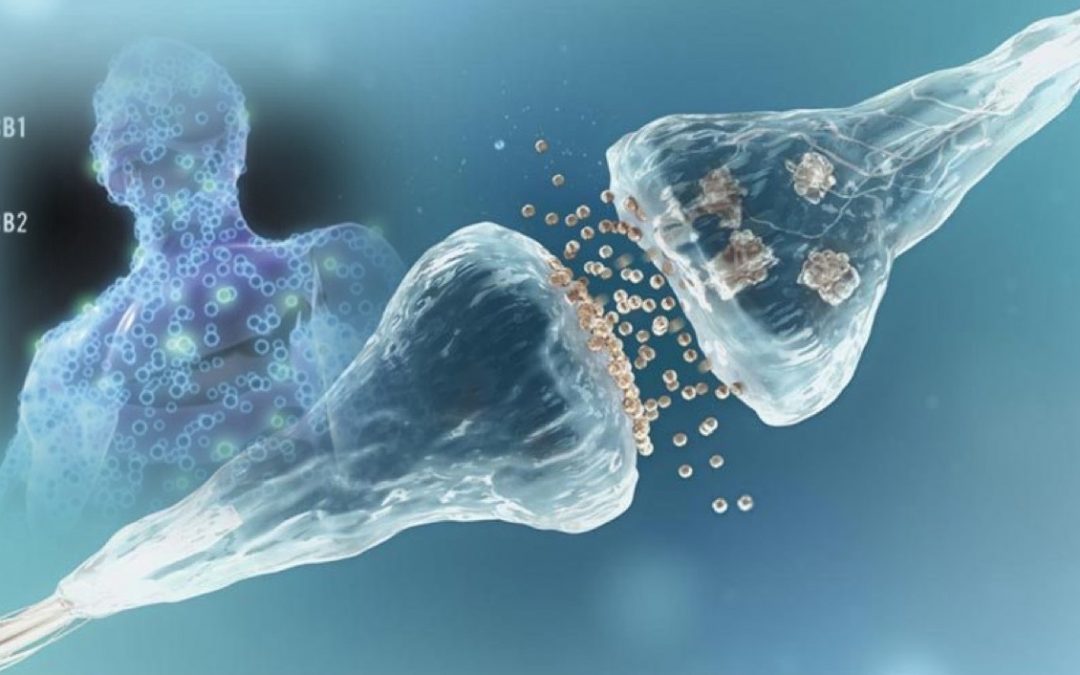
The endocannabinoid system is a regulating system designed to keep our bodily systems in homeostasis – or balance.
It consists of receptors that are present throughout the body and substances that activate the receptors. There is an abundance of these receptors in the brain and nervous system. They are also present in the immune system, stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, reproductive organs, heart and blood vessels, respiratory tract, and skin.
Our bodies make substances called endocannabinoids that activate these receptors. The most studied cannabinoids are anandamide and 2-AG. These compounds attach to the cannabinoid receptors to regulate many functions such as pain signaling, sugar and fat metabolism, muscle tone, the inflammatory response, mood, memory, appetite, GI motility, and sleep.
Certain lifestyle conditions and environmental exposures can have a negative impact on the endocannabinoid system. When it is not able to do its job, we may experience pain, muscle spasms, anxiety, and a host of other symptoms. Fortunately, certain lifestyle adjustments, including the addition of cannabis, can improve the endocannabinoid system’s ability to reduce pain, muscle spasms, anxiety, and more.
Cannabis has about 150 compounds called phytocannabinoids (phyto = plant). These compounds are only found in the cannabis plant. THC and CBD are the most studied and most familiar to us, but the plant has many other compounds that influence its effects on the body. Other well studied cannabinoids that can positively impact health include CBG, CBN, THCA, CBDA, and THCV. All of these compounds interact with our endocannabinoid system’s ability to function.
301.328.3045





0 Comments